Business
Eco-Friendly Tableware Innovation: A Technological Look at Wheat Straw vs. Bamboo Plates

In an era of environmental consciousness, the global community is steadily shifting from plastic and non-biodegradable materials to more sustainable alternatives. Whether in packaging, construction, or household items, the demand for eco-friendly materials is rising—especially in food service. Among the most promising developments are disposable tableware made from wheat straw and bamboo. These two natural materials are now competing head-to-head in a race to define the future of biodegradable plates, bowls, and cutlery.
But what sets these two options apart? What does science say about their performance, sustainability, and cost-efficiency? And how do manufacturers use technology to enhance their usability? In this article, we explore the battle between wheat straw vs. bamboo plates, examining the innovation behind each and offering a closer look into how green tech is reshaping our relationship with single-use products.
�� Related Resource: For a detailed breakdown, visit Wheat straw vs. bamboo plates on AnzhuCraft — a leading provider of eco-friendly disposable tableware.
Understanding the Need for Sustainable Materials
Single-use plastics have long been a major contributor to global pollution, especially in oceans and landfills. According to the United Nations, plastic pollution could outweigh fish in the ocean by 2050 if no action is taken. This urgent environmental crisis has driven innovation toward biodegradable alternatives such as bagasse, PLA, palm leaves, bamboo, and wheat straw.
Both bamboo and wheat straw are renewable, compostable, and relatively low-cost, making them ideal candidates for large-scale production of disposable tableware. However, they differ in sourcing, production, texture, durability, and end-of-life management.
Let’s examine how each material compares across key categories.
What is Bamboo Tableware?
Bamboo is one of the fastest-growing plants in the world. It can grow over a meter a day under optimal conditions and requires no pesticides or fertilizers. In manufacturing, bamboo stalks are harvested, shredded into fibers, and pressed into molds using heat and pressure to form plates, cups, and utensils.
�� Advantages of Bamboo Plates:
Natural Durability: Bamboo fibers are strong and resilient.
Aesthetic Appeal: Smooth finish with a natural wooden look.
Reusable Possibility: Some bamboo plates are sturdy enough for multiple uses.
Anti-bacterial Properties: Bamboo naturally inhibits bacterial growth.
�� Technological Processing:
Advanced pressing technologies and fiber treatment allow bamboo plates to resist heat, hold moisture, and stay intact without the need for synthetic binding agents.
What is Wheat Straw Tableware?
Wheat straw is the agricultural by-product left after harvesting wheat grains. Traditionally burned or discarded, wheat straw is now repurposed as a valuable biomass material. When combined with other biodegradable polymers (e.g., PLA), it can be molded into functional products like cups, plates, and trays.
�� Advantages of Wheat Straw Plates:
Zero-Waste Material: Utilizes agricultural waste that would otherwise be burned.
Microwave and Freezer Safe: Most wheat straw plates tolerate temperature extremes.
Lightweight: More convenient for transportation and storage.
Cost-Effective: Lower production cost compared to bamboo.
�� Technological Processing:
Modern pulping and bio-composite molding techniques allow wheat straw fibers to be converted into smooth, lightweight, yet strong tableware without toxic chemicals.
Wheat Straw vs. Bamboo Plates: Comparative Analysis
Here’s a feature-by-feature breakdown of how these two materials compare in the context of technology, sustainability, and consumer usage:
| Feature | Bamboo Plates | Wheat Straw Plates |
| Raw Material Source | Harvested bamboo stalks | Agricultural waste (wheat residue) |
| Eco-Friendliness | Highly sustainable and renewable | Prevents open-field burning; zero-waste |
| Production Process | Mechanical pulping, heat pressing | Biomass pulping + PLA/bioplastic molding |
| Durability | Strong, stiff, suitable for heavier meals | Lightweight, slightly more flexible |
| Microwave Safe | Depends on treatment | Generally safe up to 120°C |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable within 60–120 days | 100% biodegradable within 90–180 days |
| Price | Slightly higher | More cost-effective |
| Best For | Premium catering, reusable options | School cafeterias, fast food, home use |
Eco-Friendly Innovation: How Tech Is Enhancing Natural Materials
The application of green technology to biodegradable tableware is growing more sophisticated. Innovations include:
1. Nano-Coating Enhancements
Manufacturers use plant-based nano-coatings to make plates water-resistant without compromising biodegradability.
2. Bio-Based Binders
Both bamboo and wheat straw require binding agents. With advances in polymer science, manufacturers now use corn-starch-based bioplastics instead of petroleum-derived adhesives.
3. Infrared Drying Systems
Instead of energy-intensive ovens, companies now implement infrared drying systems that reduce carbon emissions by over 30%.
4. Smart Mold Design
Using AI and CNC machining, tableware molds are now created to minimize material waste and improve strength distribution.
Market Growth and Global Adoption
According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global biodegradable tableware market is expected to surpass $11 billion by 2032, driven by increasing bans on plastic and growing eco-conscious consumer behavior. Key growth regions include:
Asia-Pacific: Led by China and India, where agricultural waste is abundant.
Europe: Strong government policies promoting zero waste and circular economy.
North America: Increasing demand in corporate catering and organic restaurants.
Websites like are playing a crucial role in this transition by offering a wide variety of eco-friendly products to global consumers.
Use Cases: Where Bamboo and Wheat Straw Plates Shine
�� Bamboo Plates:
High-end event catering
Eco-lodges and resorts
Corporate gifts or reusable travel kits
�� Wheat Straw Plates:
School and college cafeterias
Outdoor events and picnics
Budget-conscious cafes and restaurants
Consumer Awareness: Tech Meets Transparency
Modern consumers are not just looking for “green” labels—they want transparency. Thanks to blockchain-based supply chain verification and QR-code packaging, consumers can now track the origin of their plates, the production process, and even composting instructions.
This technological transparency is becoming a key selling point in sustainable product marketing.
Challenges & Limitations
Despite their promise, both materials face hurdles:
Composting Infrastructure: Not all regions have composting facilities equipped to handle bio-based materials.
Water Usage in Processing: Bamboo, in particular, can require significant water in pulping stages.
Price Volatility: Agricultural yield variations can impact wheat straw availability and cost.
However, continuous improvements in production technology and government incentives are helping to address these challenges.
Conclusion
There is no absolute winner in the wheat straw vs. bamboo plates debate. The better choice depends on your specific use case:
For luxury appeal and durability, bamboo plates are ideal.
For affordability and minimal environmental impact, wheat straw plates are better.
What’s undeniable is that both materials represent the future of sustainable design—and they’re powered by remarkable technological advancements.
Business
From ‘For Sale’ to ‘Sold’: A Live Timeline of Home Transactions
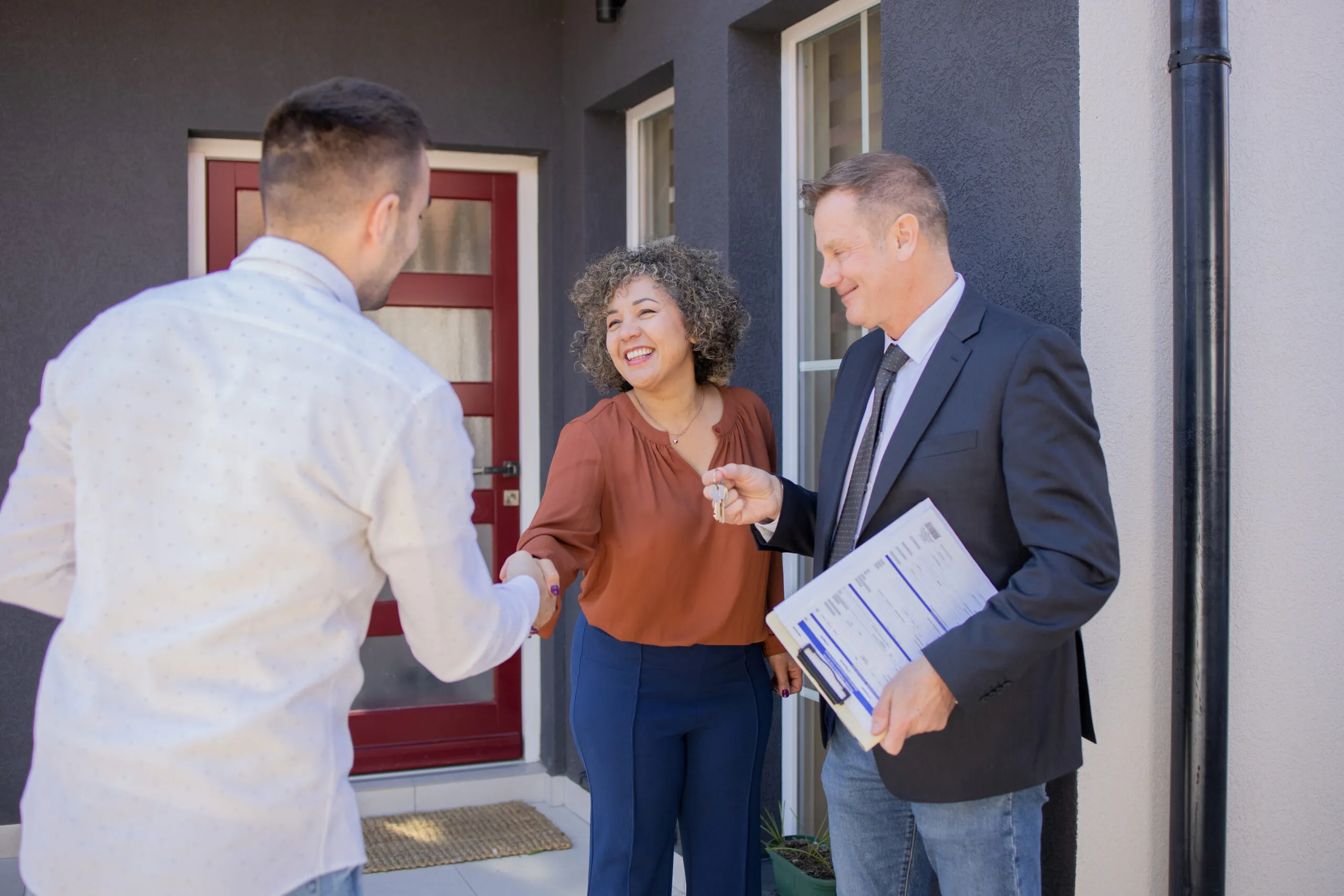

Selling a home is a journey with clearly defined stages, but each step can come with both excitement and uncertainty. By understanding what’s coming next, sellers can set realistic expectations, minimize surprises, and confidently navigate the process. For those entering the vibrant local market, partnering with West Hartford CT real estate agents The Connecticut Agency LLC can provide valued expertise and supportive guidance from the very beginning.
Homeowners embarking on a sale often find that having a strategic approach eases their transition and can maximize their returns. Clear planning, effective communication, and knowing when to seek professional help are foundational to a stress-free experience. As you move from preparing your home to closing the deal, each phase brings distinct actions and opportunities to enhance your success.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the live timeline of home transactions, arming sellers with the knowledge to make informed decisions at each milestone.
Whether you’re selling your house for the first time or are a seasoned mover, understanding this process is essential to getting from “for sale” to “sold” smoothly.
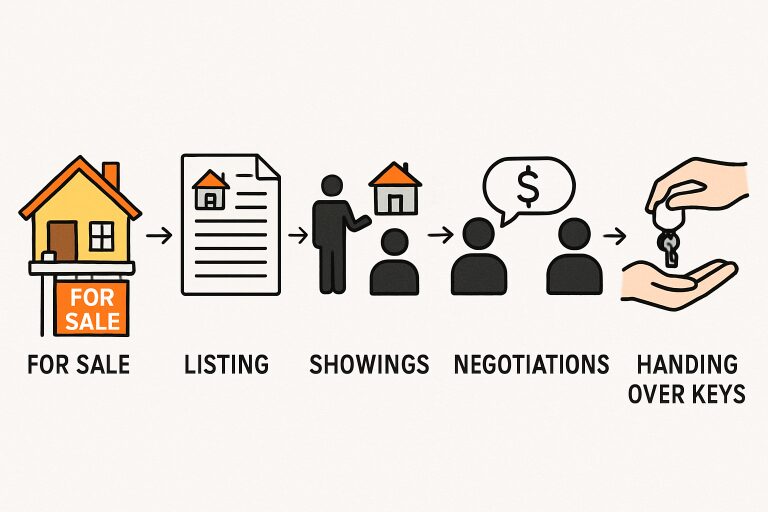
Preparing the Home for Sale
Presentation is one of the most powerful tools a seller can use. Begin by decluttering every space, making necessary repairs, and adding curb appeal. A home that’s clean, neutral, and well-cared-for will stand out in photos and in person. Minor upgrades, such as a fresh coat of paint, updated lighting, or landscaping, can also deliver a strong first impression to potential buyers.
Professional staging services are also an option, allowing your home to be showcased at its very best. According to the National Association of Realtors, 82% of buyer’s agents said staging made it easier for their clients to visualize their prospective home, often resulting in faster and higher offers.
Listing the Property
With your home ready to shine, it’s time to list it on the market. Determining the right asking price is critical—a property priced too high can linger, while one too low might leave money on the table. A market analysis with input from a skilled agent ensures your price is both competitive and realistic. High-resolution photography and a compelling, honest description of the home’s features and benefits help capture interest and set your listing apart.
Partnering with a local real estate expert means leveraging deep market knowledge, effective negotiation skills, and professional marketing resources that may not be accessible to homeowners alone.
Marketing and Showings
Exposure is key to generating interest and offers. A combination of online listings, social media campaigns, email marketing, open houses, and signage draws attention to your property. Scheduling private showings allows prospective buyers to explore the home, ask questions, and envision how it fits their needs.
Flexibility during this phase is crucial—accommodating last-minute showing requests or weekend open houses ensures you don’t miss motivated buyers. Regular communication with your agent can also help you adapt marketing strategies as needed to maximize traffic.
Receiving and Negotiating Offers
With interest established, offers may begin to arrive. Each offer will contain specifics on price, conditions, closing dates, and other terms. Evaluate all the details, not just the dollar amount—sometimes a slightly lower offer with fewer contingencies or a faster closing can be the best choice. Negotiations often follow, involving counteroffers and clarifications. Successful negotiations typically require collaboration and realistic expectations from both sides, aiming for a win-win situation and a swift agreement.
Under Contract and Due Diligence
After an offer is accepted, the property moves into the “under contract” stage. This is when buyers do their due diligence, which may include home inspections, appraisals, and securing financing. Inspections can uncover issues leading to further negotiations or repair requests. The appraisal confirms the property’s value for the lender; if it comes in lower than the agreed price, renegotiation may be required. Staying responsive and flexible throughout this phase can prevent delays and complications.
Closing the Sale
The closing process finalizes the transaction. During this period, both parties review and sign numerous documents, title searches are conducted, and funds are transferred. Common participants include real estate agents, attorneys, title companies, and lenders. Ensuring all contingencies are satisfied—and being prepared to quickly resolve last-minute issues—will help you reach this goal. On the day the keys are handed over, your home is officially sold.
Business
From On-Prem to Cloud: How SASE Simplifies Security for Hybrid and Remote Workforces
A Shift in the Modern Workforce
The dramatic evolution of work environments in recent years has pushed organizations to adapt to new modes of operation rapidly. With remote and hybrid work models moving from an emergency solution to a long-term strategy, IT teams face increasing pressure to deliver secure access to data and applications across varied locations and devices. SASE network security has emerged as a leading solution, enabling organizations to address these challenges with a unified, cloud-first approach that follows the user, wherever work occurs.
As many organizations embrace flexible work arrangements, the traditional boundaries of the enterprise network have all but vanished. Employees tap into corporate resources from home offices, coworking spaces, and on the go—often relying on personal devices or insecure connections. This paradigm shift has compelled organizations to reassess their approach to protecting critical assets and controlling user access beyond the confines of an office, making holistic security more crucial than ever.
Traditional Security Models Struggle to Keep Pace
Classic perimeter-based security solutions, such as firewalls, VPNs, and network access controls, were designed for centralized office environments. As workforces grow more distributed, these tools become increasingly ineffective. Data flowing far outside company walls and traffic between cloud applications all challenge the effectiveness of on-premises security architectures. VPN solutions, once a mainstay of remote work, now struggle under demanding workloads, offer inconsistent user experiences, and introduce vulnerabilities when not well managed. According to an analysis by CSO Online, companies relying solely on traditional defenses face higher risks of data breaches and limited visibility over their environments.
What Makes SASE Different?
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) fundamentally reimagines security and networking for today’s needs. By unifying advanced networking functions, such as SD-WAN, with cloud-delivered security, including firewall-as-a-service, secure web gateways, and zero-trust network access, SASE creates a holistic defense perimeter anchored in the cloud. Security policies and access controls are not limited by physical location, but rather by context, including user identity, device security posture, and real-time risk assessment. This enables organizations to provide secure, optimized access to resources, regardless of where employees or workloads reside.
Simplified Access and Security for Every User
Zero trust is at the core of the SASE model. Instead of inherently trusting devices or users simply because they connect from inside the network, SASE evaluates each interaction. This principle is especially effective for organizations with employees moving between multiple environments. Every application request is fully authenticated and authorized before access is granted. It ensures consistent enforcement of security policies, regardless of whether an employee is connecting from the corporate office, a hotel room, or a coffee shop. Workflows remain seamless, user experiences remain fast and reliable, and sensitive data stays protected everywhere.
Real-World Benefits of SASE for Hybrid Teams
Adopting a SASE framework yields tangible results for organizations managing hybrid and remote workforces. Companies report increased visibility into user activity and network traffic, which enhances their ability to track threats and respond to incidents swiftly. Policy management becomes far simpler, as security and networking configurations are handled through a single, central dashboard—allowing global rule enforcement and streamlined auditing. The risk of exposure to new vulnerabilities is minimized through ongoing threat intelligence updates, patch management, and automated response capabilities. Gartner research has highlighted that SASE helps IT teams deliver improved cloud application performance—critical for productivity when access happens from virtually anywhere.
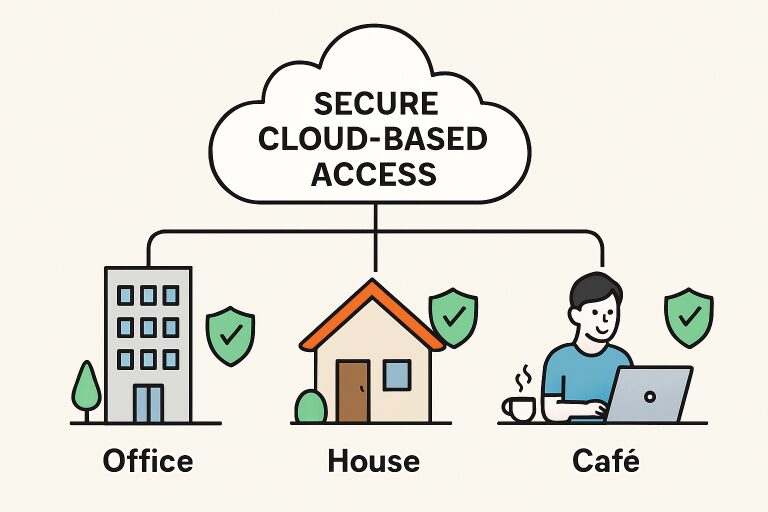
Streamlining Compliance and Reducing Overhead
SASE simplifies compliance for organizations facing evolving regulatory landscapes. Instead of juggling multiple point solutions for data loss prevention, firewall management, and identity protection, IT teams can implement and prove controls from a consolidated interface. This unified foundation makes tasks like policy enforcement, user auditing, and evidence collection easier and less time-intensive, which in turn reduces the risk of fines and helps demonstrate ongoing regulatory compliance in sectors like healthcare, finance, and retail.
Key Features to Consider When Evaluating SASE Solutions
- Integrated Security: Choose platforms that offer robust threat protection, data loss prevention, and secure web gateways in a single solution.
- Scalability: Prioritize cloud-native architectures that dynamically adjust to your organization’s changing needs—supporting small teams or thousands of new endpoints efficiently.
- Zero Trust Support: Ensure the solution implements strict authentication and granular access controls based on real-time user and device context.
- Performance Optimization: Look for global presence, intelligent routing, and bandwidth management that keep cloud applications responsive for all users.
- Centralized Visibility: A single-pane-of-glass dashboard should deliver clear insight into all traffic and security events, simplifying monitoring and remediation efforts.
Steps to Get Started with SASE
- Assess Your Current Architecture:Catalog legacy systems, workflow gaps, and security pain points in your existing environment.
- Define Your Security Policies:Document clear, risk-based guidelines for application access, device trust levels, and incident response procedures.
- Choose the Right Partner: Select SASE vendors that align with your security standards, offer proven performance, and deliver responsive support.
- Pilot and Expand: Launch an initial rollout with a group of users, gauge outcomes, and systematically scale implementation based on feedback and results.
The Future of Secure Access for Distributed Workforces
The transition from on-premises security to cloud-first models is rapidly accelerating. SASE not only meets the current needs of hybrid and remote workforces but also positions organizations to stay ahead of future threats. By providing secure, agile, and scalable access to organizational resources—regardless of location—businesses can embrace new ways of working while safeguarding their critical data. As hybrid work establishes itself in the business landscape, rethinking security through the lens of cloud-based SASE solutions is becoming a crucial competitive advantage.
Business
The Benefits of Working With a Wealth Planner for Long-Term Success

Financial planning services help individuals and business owners effectively manage their assets throughout their lifetime. An experienced financial planner assesses your current financial situation to determine investment strategies that align with your goals. Here are some benefits of working with a wealth planner for long-term success:
Investment Management
Professional planners help affluent individuals and companies invest in the right sectors by reviewing market trends and investment opportunities. They can advise you on where to allocate your funds, including stocks, bonds, or real estate, to help increase your assets. As markets change, a wealth planner reviews your portfolio to determine whether it matches your goals. These experts can adjust your holdings by suggesting you sell or buy stocks based on your risk tolerance. If you want to build an education fund or preserve your capital, financial advisors work with you to manage risks while maximizing profit.
Tax Planning
With higher incomes and complex investment portfolios, tax laws often become more challenging to navigate. Wealth planners help identify areas where taxes may be minimized, such as through charitable giving for individuals and families. If you own a business, an advisor can help you choose the right structure, such as a limited liability company, which offers tax advantages. Placing your assets in the right accounts helps reduce your tax liability each year and grow your wealth over time. If you’re planning to sell your business or pass it on, a professional can establish a trust to streamline the transfer and minimize fees.
Estate and Trust Planning
Once you’ve generated significant wealth, financial planning services help protect what you’ve built and pass it on to the next generations. Some key estate planning options include:
- Trusts: If you own a business and other assets, trusts can safeguard them from taxes, lawsuits, and creditors who would otherwise deplete your wealth.
- Wills: With the right estate plan, transferring wealth to your loved ones often results in fewer disputes and losses. It helps determine who receives what, when, and how, according to your wishes, once you pass away.
- Charitable giving: Financial planners also help you support local organizations through charitable trusts, foundations, or donations.
Retirement Income Planning
Whether you have investment accounts, pensions, or savings, a wealth manager helps you plan your retirement income. They review these assets to create a financial plan that aligns with your lifestyle and maximizes your financial returns. To keep the money working for you, wealth planners suggest withdrawing or investing in accounts at specific times to maximize revenue.
A cash flow analysis helps financial advisors understand your monthly expenses and your income sources. This allows them to recommend a suitable savings plan or investment opportunities. When claiming benefits from Social Security and pensions, they provide information about beneficial times to begin receiving payments.
Get Started With Financial Planning Services
A wealth planner helps you prepare for retirement, allocate funds well, and manage different risks. To protect your assets and distribute them when the time comes, these professionals create several legal documents. If you’re looking to manage your wealth, call a trusted company today to learn more about their financial planning services.
-

 Tech6 months ago
Tech6 months agoSotwe STW Explained How a Radical Platform is Redefining Online Expression
-

 Entertainment8 months ago
Entertainment8 months agoHow Do I Turn On the Beatbot?
-

 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoAre B750 Motherboard A Good Choice – A Complete Overview!
-
 Blog1 year ago
Blog1 year agoHow To Find My Motherboard Model And Bios Version – A Detailed Overview!
-

 Motherboard Guide1 year ago
Motherboard Guide1 year agoAre Gigabyte Motherboards Good – A Comprehensive Review!
-

 Blog3 months ago
Blog3 months agoHer Love Is A Kind Of Charity Password – The Hidden Meaning Behind the Phrase!
-
 Motherboard Guide12 months ago
Motherboard Guide12 months agoB75 Motherboard What Generation Cpu Is Supported – B75 Motherboard Cpu Support!
-
Motherboard Guide4 months ago
The Ultimate Croatia Travel Guide for First-Timers: Everything You Need to Know Before You Go

